Business


-

Our Business
スペースデブリ除去事業
Space Debris Removal Business
Space Debris Removal Business

-

Our Business
衛星ライダー事業
Satellite LiDAR Business
Satellite LiDAR Business

Our Business
01
スペースデブリ除去事業
Space Debris Removal Business
Space Debris Removal Business

衛星の打ち上げ数が急増するとともに、運用を終えた人工衛星や衛星の運用中に放出された部品など、今、「宇宙ゴミ(スペースデブリ)」の問題が深刻化しています。その数は、10cm 以上のものが 40,500個程度、1〜10cm のものが 110万個程度、1mm〜1cm のものが1億 3,000 万個以上と推測されるほど、膨大な量に及びます。
今後も、安全で持続可能な宇宙環境を維持していくためには宇宙ゴミ削減に向けた対処が不可欠です。
Orbital Lasers はこの問題の解決に向けて、独自に高度なレーザー技術を開発し、スペースデブリ除去事業を展開しています。
As the number of satellite launches increases, the problem of "space debris" including decommissioned satellites and fragments from satellite operations—poses a growing threat to space safety. Currently, there are an estimated 40,500 objects larger than 10 cm, 1.1 million pieces between 1 cm and 10 cm, and over 1.3 billion particles between 1 mm and 1 cm orbiting Earth. To preserve a safe and sustainable space environment, space debris removal is essential. Orbital Lasers is addressing this issue by developing advanced laser technology to lead the space debris removal business, ensuring long-term safety in orbit.

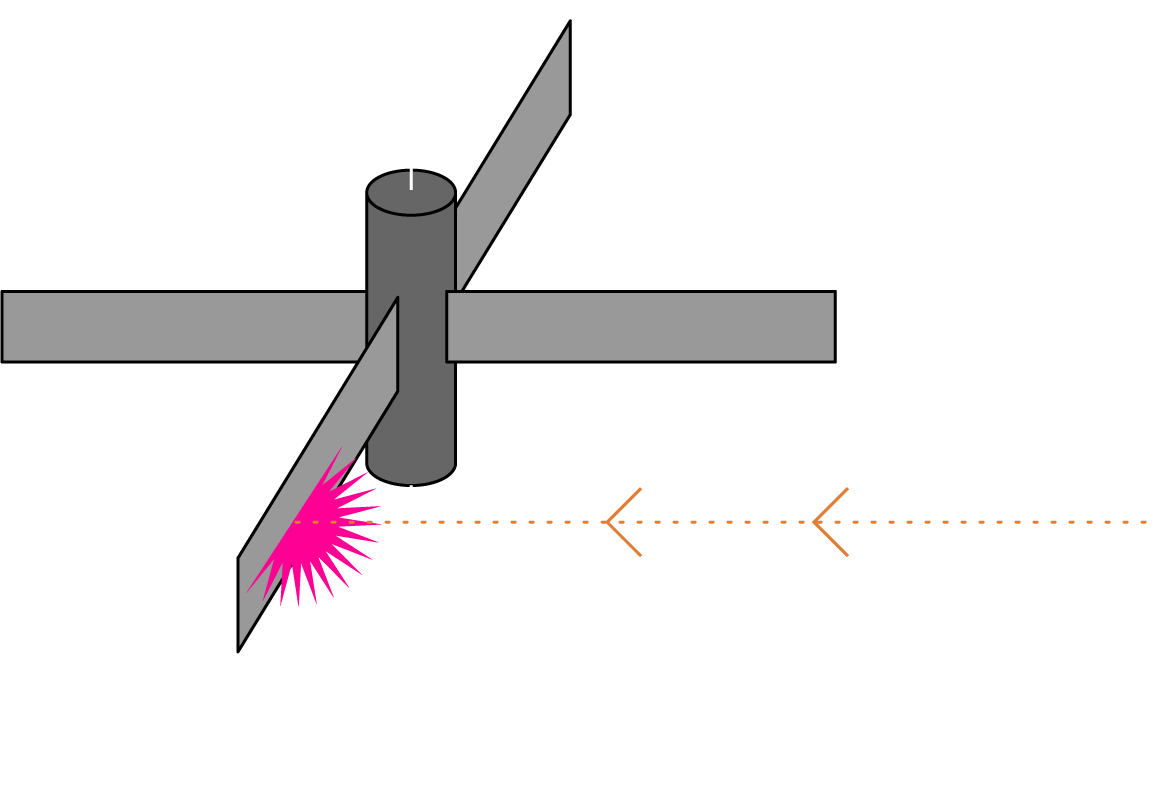
独自の衛星レーザー技術を活用した
スペースデブリ除去手法
Unique Space Debris Removal Method Utilizing Proprietary Satellite Laser Technology
スペースデブリはコントロール不能となったロケットや衛星といった大型なものから、数cmクラスの微小な破片まで様々なものがありますが、レーザー技術を用いて、あらゆるデブリの軌道・運動制御を可能とします。特に、回転運動を伴うデブリは物理的な捕獲が困難ですが、レーザーによりデブリの静定化を安全に行うことが可能となります。
Space debris encompasses everything from large, uncontrollable rockets and defunct satellites to small fragments only a few centimeters in size. With the use of proprietary satellite laser technology, it’s now possible to manage the orbit and movement of various types of space debris. Lasers are especially effective for stabilizing rotating debris, which is typically challenging to capture through physical methods. This innovative approach enables the safe and efficient control of debris, advancing the goal of space debris removal and ensuring the long-term sustainability of Earth's orbit.
レーザー方式の3つの利点
Three Advantages of the Laser Method for Space Debris Removal
-
Advantage 01
高い安全性
Enhanced Safety
遠隔からデブリに対して
レーザー照射するため、衝突リスクなく
対象衛星を移動させることが可能Lasers can be targeted at debris from a distance, allowing for satellite adjustments without the risk of collisions.
-
Advantage 02
回転物体への適用
Effective for Rotating Objects
適切な場所、タイミングで
レーザー照射することで、
安全に回転運動を止めることが可能By precisely timing and aiming the laser,
we can safely halt the motion of rotating debris. -
Advantage 03
高い経済性
Cost-Effective Solution
どんな物体にも適用可能であり、
除去対象となる衛星側の設計変更や
アタッチメントが不要This laser method is versatile and can be applied to various objects without requiring any design modifications or attachments to the satellites being targeted for removal.
Issue
宇宙空間には大量のゴミがあり、
年々増え続けている...
The amount of debris in space is vast and continues to grow each year,
posing significant risks to satellites and other space operations.


宇宙ゴミの数
Number of Space Debris
2024年時点、ESA公表情報に基づく
As of 2024, Based on ESA Public Data
-
約40,500
About40,500
-

約
1 10万About
1 .1 Million -

約
1 .3億About
1 30Million
-
軌道が判明している
(カタログ化)宇宙物体Cataloged Space Objects
and Their Orbits
約36,000
Approximately 36,000
2024年時点、ESA公表情報に基づく
As of 2024, based on ESA public data
-
運用中の衛星
Active Satellites
約
1 0,000About
1 0,0002024年時点、ESA公表情報に基づく
As of 2024, based on ESA public data
-
破片を生み出した
分裂・爆発・衝突・異常等の
イベント数Number of Events Involving Fragmentation, Explosions,
Collisions, or Anomalies
650回以上
Over 650
2024年時点、ESA公表情報に基づく
As of 2024, based on ESA public data
-
宇宙空間に
打ち上げされた物体数Total Objects Launched into Space
1957-2021
19,000超
Over19,000
2024年時点、ESA公表情報に基づく
As of 2024, based on ESA public data
-
メガ・コンステレーションの
衛星数Number of Satellites in Mega Constellations
2021-
70,000以上*
Over70,000*
*2024年時点における各社計画機数の合計値(当社調べ)
*According to in-house research, this figure is based on the projected number of satellites planned by various companies as of 2024.
今後10年の打ち上げされる衛星は過去60年で⼈類が打ち上げてきた衛星の数を
⼤幅に上回り、低軌道では急速に衛星の混雑化が進む
Over the next 10 years, the number of satellites launched is expected to
far surpass the total launched in the past 60 years, resulting in rapid congestion in Low Earth Orbit.
Solution
Orbital Lasersによる
「レーザーアブレーション」方式を
活用したデブリ除去
Laser Ablation for Space Debris Removal by Orbital Lasers
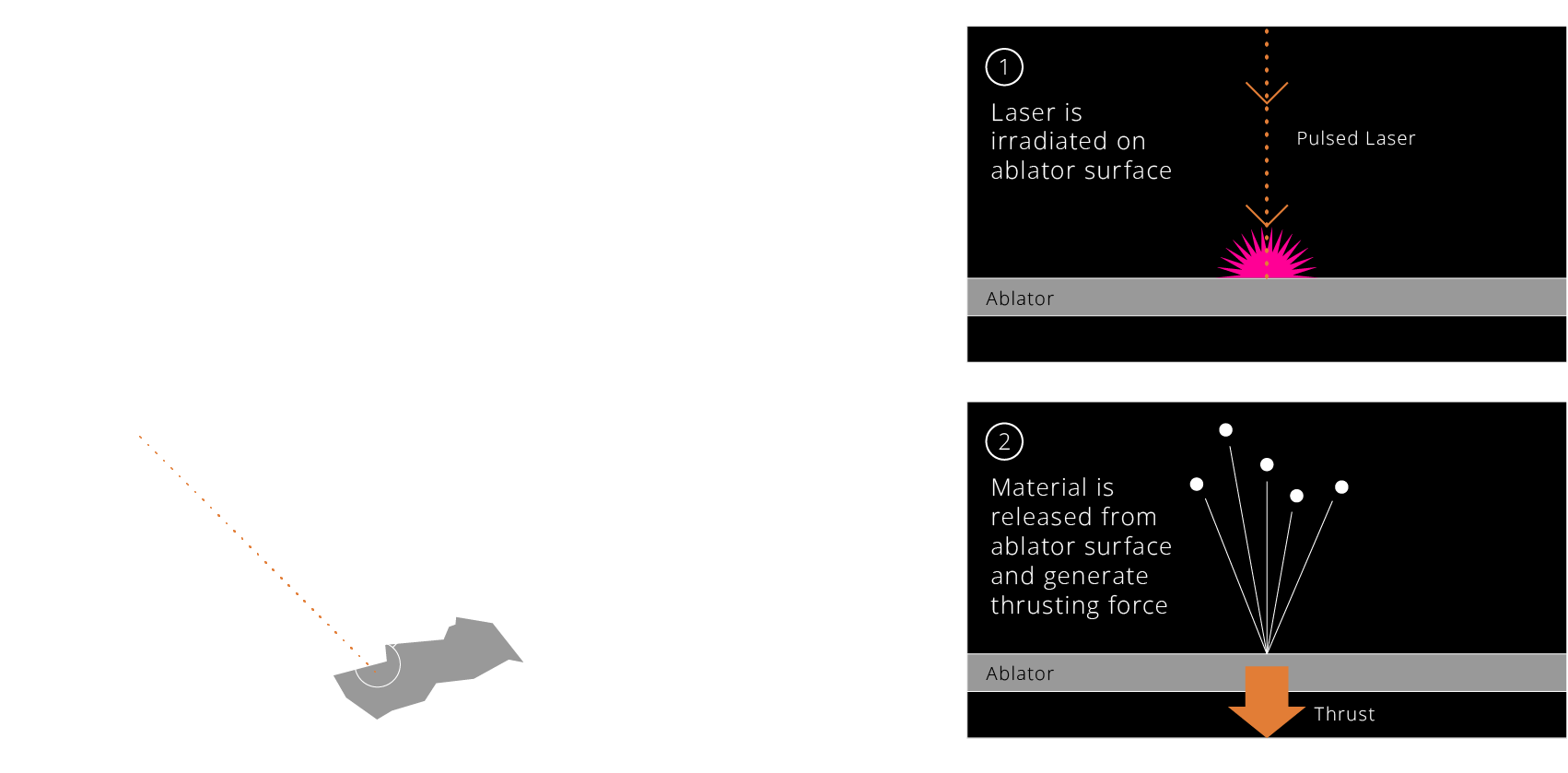
レーザー光を対象物に照射することで、その表面の物質をプラズマ化・気化させる技術。宇宙空間でアブレーションを起こすことで、わずかな推力を生じさせることが出来る。安全にデブリを移動させたり、回転運動を低減することが可能となる。
The laser ablation technique directs laser light at a target object, vaporizing and ionizing its surface material to generate thrust. This method allows for the safe relocation of space debris and the reduction of its rotational motion, enhancing the safety and sustainability of low Earth orbit. By harnessing laser ablation, Orbital Lasers is at the forefront of tackling the growing challenges of space debris.
実証実験
Demonstration Experiment

Our Business
02
衛星ライダー事業
Satellite LiDAR Busines
Satellite LiDAR Business

衛星放送や気象予報、GNSS による位置情報の提供など、衛星を活用したサービスは現在、社会や経済を支える重要なインフラであると同時に、私たちの暮らしに欠かせない存在になっています。
Orbital Lasersの高度なレーザー技術は衛星搭載型ライダー(衛星ライダー)にも応用可能です。
衛星ライダーは、地表面に向けて照射したレーザーの反射光の時間差をもとに、地表面の高度を精緻に計測することが出来ます。
衛星ライダーを活用した計測データは、森林管理、森林バイオマス推定、国土管理、盛土・切土のモニタリング、土砂崩壊リスク検知、都市デジタルツイン、3D マップ作成などの多岐に渡る分野で活用・応用することが可能です。
Orbital Lasersは、将来的に小型ライダー衛星コンステレーションを構築・運用し、世界中のあらゆる場所の高度情報を精緻に取得し、ユーザーが使いやすい形でデータを提供していきます。
Satellite-based services, including broadcasting, weather forecasting, and GNSS for location services, have become vital infrastructure, supporting society and driving economic growth. Orbital Lasers' advanced laser technology can also enhance satellite-mounted LiDAR (Satellite LiDAR). This technology enables precise measurement of surface elevation by calculating the time difference of laser reflections from the ground.
LiDAR-based measurement data has diverse applications, including forest management, biomass estimation, land management, embankment and excavation monitoring, landslide risk detection, urban digital twins, and 3D mapping.
Looking ahead, Orbital Lasers plans to develop and operate a small LiDAR satellite constellation, providing accurate altitude data for any location on Earth in an accessible format.

リモートセンシングを活用した3次元測量
3D Surveying Using Remote Sensing Technology
小型ライダー衛星コンステレーションにより、世界中のどんな場所でも高さ分解能がcm級の3次元計測が可能となります。オーダーから計測、データ生成・提供までを自動化することで、快適なユーザーエクスペリエンスと低コスト化を実現します。
With a small LiDAR satellite constellation, 3D measurements can be conducted with centimeter-level height resolution from any location on Earth. Automating the entire process—from order placement to measurement, data generation, and delivery—ensures a seamless user experience while minimizing costs. This innovative approach will enhance data accessibility and accuracy for a variety of applications, including mapping, urban planning, and environmental monitoring
- Satellite
- Aircraft
- Drone

Use Case
-
Real 3D Earth
High-Precision 3D Mapping of Earth
小型ライダー衛星コンステレーションにより世界中のあらゆる場所における高精度3D地図を作成。高頻度に更新することで、3次元的な変化も捉えることが出来ます。
A small LiDAR satellite constellation will facilitate the creation of high-precision 3D maps for any global location. These maps can be frequently updated, capturing three-dimensional environmental changes efficiently.
-
樹高測定による
カーボンクレジット評価Accurate Carbon Credit Assessment Through Tree Height Measurement
定期的に樹高を正確に測定し、森林の炭素吸収量を推定します。これにより、カーボンクレジットの算定が精密かつ効率的に行えます。さらに、森林伐採や森林火災後の再生状況の把握といった環境監視にも活用できます。
Regularly measuring tree heights allows for accurate estimates of forest carbon absorption, enabling precise carbon credit assessments. This data is also valuable for environmental monitoring, such as evaluating forest regrowth after deforestation or wildfires.

-
海底面3D
Seabed Topography Mapping
衛星ライダーは波長によっては水中も透過することができ、それによって浅瀬や沿岸部の海底地形を測定できます。海洋環境の保全、航路計画、沿岸開発などに重要な情報を提供します。
Certain wavelengths of satellite LiDAR can penetrate water, allowing the measurement of seabed topography in shallow waters and coastal areas. This data is essential for ocean conservation, route planning, and coastal development projects.

-
ドローン自動航行用MAP
Enhancing Autonomous Drone Navigation with 3D Mapping
衛星ライダーにより複雑な地形や高密度な都市環境も高精度に3次元計測することができ、そのデータをドローンの自動航行システムに統合することで、ルートを安全かつ効率的に設定できます。障害物回避や経路最適化に役立ちます。
Satellite LiDAR enables high-precision 3D mapping of complex terrains and densely populated urban environments. Integrating this data into autonomous drone navigation systems optimizes and safely plans routes, aiding in obstacle avoidance and path efficiency.

-
国土管理
Land Management
国土全体の地形(河川、海岸、山間部等)を高精度かつ安価に定期計測することで、政府や自治体、民間企業等が行う災害リスクの評価や地形変動のモニタリング、インフラ整備計画に重要な情報を提供します。
By regularly measuring the topography of entire nations, including rivers, coastlines, and mountainous regions, governments and companies can obtain valuable data for disaster risk assessment, terrain change monitoring, and infrastructure planning.

-
都市計画
Urban Planning and Disaster Prevention
衛星ライダーによる高頻度計測で、防災対策やデジタルツイン技術を活用したスマートシティに重要な3次元データを常にフレッシュな状態にすることが出来ます。
Frequent measurements using satellite LiDAR ensure that 3D data crucial for disaster prevention and smart city initiatives, such as digital twins, remains consistently up-to-date.